CHAPTER 3: COMPLETE OFF-PAGE SEO FREE GUIDE
Off-page SEO is covered in detail in this guide for 2022. You will precisely discover how to create the kinds of off-site signals that Google wants to see in this new tutorial, including:
What is Off-Page SEO?
Off-page The technique of optimizing web | blog pages outside of your website by obtaining links back to it is known as SEO. Back-link is the name given to this link.
Why Is Off-Page SEO Important?
Google’s algorithm is still built around off-site signals like backlinks. In reality, the amount of backlinks and Google rankings clearly correlate, according to our 2020 search engine ranking criteria study. For instance, Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines heavily consider a site’s reputation off-site when determining whether or not it can be trusted. (This is referred to as “Reputation Research”).Looking at online reviews is a component of “reputation research”:
Backlinks &link building
One of the most crucial elements of search engine optimization, backlinks, will be covered in the sixth chapter of our SEO guide for beginners.
Chapter navigation
- What is a backlink?
- Types of links
- Link profile
- Attributes of a valuable backlink
- Should you do link building?
- Link building strategies
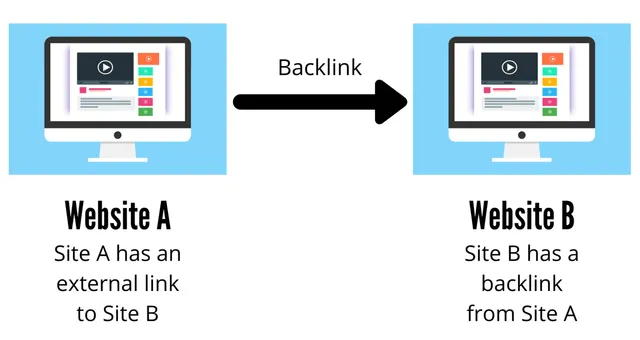
What is a backlink?
 A link from one page to another is known as a backlink. We refer to page B as having a backlink from page A if page A connects to page B. One of the most crucial SEO signals is the number of backlinks. Rankings and the quantity and quality of backlinks are directly correlated.
A link from one page to another is known as a backlink. We refer to page B as having a backlink from page A if page A connects to page B. One of the most crucial SEO signals is the number of backlinks. Rankings and the quantity and quality of backlinks are directly correlated.
Why are backlinks so important?
Since the beginning, backlinks have had a significant impact on search engine algorithms. They serve as scholarly citations. The creators of search engines understood that a page is important and trustworthy if numerous reputable resources connect to it.
Connect equity
The power a page transfers to another page through a link is known as link equity, often known as “link juice.”
PageRank on Google
To assess the relative relevance of web sites in search results, Google developed an algorithm called PageRank in the beginning. This algorithm takes the quality and quantity of backlinks into account.
The following three elements have an impact on a page’s PageRank:
- Backlink count: The more links a page has, the better.
- The value (referred to as link equity) is divided among all the pages that are connected from the linking page, depending on the number of links on the connecting page.
- Link equity is increased when a backlink comes from a page with a higher PageRank.
PageRank measurement
The PageRank algorithm is not to be confused with a previous statistic of the same name that Google used to display the rankings of the pages from 0 to 10. Although the PageRank metric was dropped, the PageRank algorithm is still used by Google to determine rankings, therefore they are not equivalent.
Types of links
Links can be categorized into a number of different groups. The first ones you should be aware of are as follows:
Compared to external links
This is a rather clear one.
A link from one page to another within the same website is called an internal link, whereas a link from another website is called an external link.
Non-follow links
 A link with the rel=”nofollow” property in its HTML code is referred to as a nofollow link.
A link with the rel=”nofollow” property in its HTML code is referred to as a nofollow link.
Google first implemented it in 2005, and it instructs search engines not to give the linked page any link equity. The nofollow attribute may be used in the following situations:
- Links in comments – by devaluing links in comments, it aids in the fight against comment spam.)
- You won’t transgress Google’s guidelines regarding the purchase of backlinks by using the nofollow attribute on affiliate and sponsored links.
- Links to websites you don’t want to recommend — occasionally, you must link to pages you don’t want to recommend.
- Technically, “dofollow” backlinks don’t exist because there isn’t a “dofollow” parameter. The phrase is used informally to distinguish between connections that pass link equity and ones that are nofollow.
Nofollow links don’t pass authority, although they can still be useful for other reasons:
- They might act as a tip for Google, which declared in 2019 that nofollow links will be treated as such in order to better understand and analyze links.
- They may not give you any “SEO points,” but they can still send you relevant visitors. A nofollow link can do this.
- They widen the scope of your link profile. Every link profile naturally contains nofollow links, thus it would be strange to have any missing (see the point below).
Link profile
You should also be familiar with the term “link profile” in SEO. It serves to identify each and every link that leads to your website. Your rankings are directly correlated with the caliber of your link profile.
What characteristics mark a quality link profile?
- Diverse: A healthy link profile includes both conventional and nofollow links, as well as anchor texts that are naturally occurring.
- Quality backlinks: A good link profile includes links from reliable, pertinent sources.
On the other hand, an excessive number of low-quality connections from spamming websites will either be disregarded or detrimental to your website.
Anchor text
 A hyperlink’s visible and clickable component is the anchor text. It enables crawlers to indicate what the linked page is about.
A hyperlink’s visible and clickable component is the anchor text. It enables crawlers to indicate what the linked page is about.
Different sorts of anchor texts are distinguished here:
- brand, such as “RS Softwire”
- A perfect match, such as “SEO guide”
- Partially matching terms, such as “practical SEO tutorial”
- Generic — for instance, “read more”
- “https://rssoftwire.com/seo-guide/” is an example of a naked URL.
You might improve your position in the search engine results if more websites link to you and employ pertinent keywords in their anchor texts. This does not imply that you should make every effort to obtain anchor texts that are keyword-rich.
Attributes of a valuable backlink
Backlinks are not created equally.
Two backlinks may have different values (and pass varying amounts of link equity) based on a variety of circumstances, in addition to the obvious variations between internal and external connections and standard vs. nofollow links.
Here is an example of a useful backlink:
1. Relevant
Topically pertinent backlinks are valuable. The linking page should cover a subject that is related to or the same as that of the linked page.
For instance:
The former backlink is far more beneficial if you have an article on hiking advice and two backlinks, one from an outdoor sports piece and the other from a political post.
2. From an authoritative website
Pages with high-quality links pointing at them also convey additional link equity to your page, as we’ve already discussed with PageRank.
The value of the backlink increases with the authority of the connecting page. Although there isn’t a Google official statistic that would indicate the authority of a page, there are various metrics provided by third-party applications that can aid in your evaluation.
3. Unique
There are several ways to discuss a backlink’s uniqueness:
Website level
A backlink from a website that hasn’t previously linked to you is typically more useful than one from a site that has. Ten hyperlinks from ten distinct websites are preferable to fifty from one single website.
Page level
The link that shows initially may be more valuable than the second if you have two links coming from the same page. (Back in 2009, Google only counted the first anchor text. Although we don’t know how they treat them now, we can infer that nothing has changed.)
Number of other links
Last but not least, the connected pages all receive the same amount of PageRank. A backlink from a page that links to 3 resources and a backlink from a page that links to 30 resources are very different from one another.
4. Placed near the top in the body
A good link will drive traffic to your website.
Not just for the immediately apparent reasons (more visitors), but also from the perspective of SEO. In order to determine how likely it is for a user to click on a link, Google uses a model known as the “Reasonable Surfer”: “The amount of PageRank a link might pass along is based upon the chance that someone might click on a link.”
5. Has relevant anchor text
When building links, anchor text is crucial.
It goes without saying that a backlink with anchor text that is pertinent to the linked page is worth more than one with an unrelated or generic anchor. This also holds true for the content that precedes the link, as links may have context.
Should you do link building?
 In a perfect world, producing excellent content would be sufficient to obtain high-quality backlinks.
In a perfect world, producing excellent content would be sufficient to obtain high-quality backlinks.
The truth is a little more nuanced:
Without extra work on your part, obtaining quality backlinks is very difficult, if not impossible. particularly for fresh websites. Without any backlinks, getting ranked is exceedingly difficult, if not impossible. particularly for fresh websites. Because of this, link building is essential to SEO. But there is some debate surrounding it as well. Does this imply that you can’t make any attempts to control the quantity and caliber of your backlinks? In our opinion, no. Not all link-building strategies are spammy or deceptive
Should you buy links?
Purchasing backlinks is a completely different chapter right now. The majority of SEO professionals will advise you against it.
Here are the two main drawbacks of link purchasing:
- It’s dangerous since Google strongly discourages buying backlinks, and if they catch you, your website might never fully recover.
- It is pricey – a high-quality backlink will set you back at least $100, and frequently much more. Of course, getting just one backlink won’t help you rank, so you’ll need to spend a lot to see any progress.
However, the link selling sector is still very active, and acquiring backlinks is a widespread activity. The choice is ultimately up to you. Just keep in mind that it’s a pretty hazardous tactic that might not be successful in the long term.
Link building strategies
There are many link-building strategies, hacks, and tips available (you may get ideas from our comprehensive list of more than 60 link-building strategies). We’ll go through the three most popular, highly effective tactics for SEO in this post.
Linkable resources
The most organic link-building strategy is to produce a special and worthwhile piece of content, or “linkable asset,” that will draw in backlinks. Any piece of material can be a linkable asset, but particular kinds of content are ideal for this. These consist of:
- ultimate guides
- large lists
- research using distinct data
- directories of resources
- free tools
Finding websites that might link to you and contacting them is the next step (more on that in a while).
Guest posting
 The most common link-building strategy is undoubtedly guest posting (or guest blogging). It is scalable and somewhat straightforward (albeit not simple).
The most common link-building strategy is undoubtedly guest posting (or guest blogging). It is scalable and somewhat straightforward (albeit not simple).
Summary of how guest blogging operates:
A guest post is written for Site B by an author from Site A. His personal website is linked in the post. Site A receives a free hyperlink, while Site B receives free content. Win-win.
How do you locate blogs that allow guest posts in your niche?
Try to utilize particular search criteria to narrow down the results to those that are pertinent to you. as in “your specialty” and “write for us.” After discovering them, review their guest posting policies and get in touch with the owner to pitch a guest article.
Competitor’s backlinks
A smart technique to locate websites that might link to you is to search through the link profiles of your competitors. (After all, they did link to a page with a similar topic, right?) To locate the backlinks of your rivals, all you need is a backlink analyzing program (like LinkMiner).
Either type the domain into your browser: The program will display all backlinks along with some other details (the authority, anchor text, attributes, etc.)
Consider the following while examining the backlinks of your competitors:
- Would a backlink from this page be appropriate for your content?
- Link strength: How authoritative is the page that is linking?
- Will you be able to acquire the same backlink?
The following phase is the so-called email outreach, which entails getting in touch with website owners to ask them to either add your backlink as an additional resource or remove the competitor’s backlink (also known as The Skyscraper Technique).
The Skyscraper Technique
The Skyscraper Technique operates as follows, according to Brian Dean of Backlinko:
- Find the best article on a particular subject, then create something even better (see the 10x content technique).
- next get in touch with every website linked to your rival and request that they link to you instead.
Analytics & metrics
 The final chapter of our comprehensive SEO book will examine the crucial data analytics tools and metrics that each website owner should be familiar with and employ.
The final chapter of our comprehensive SEO book will examine the crucial data analytics tools and metrics that each website owner should be familiar with and employ.
Chapter navigation
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics
- Rank tracking
- Analytics tips and best practices
An essential component of search engine optimization is website analytics.
In SEO, the adage “What gets measured gets improved” is unquestionably true. Your website’s performance may be tracked and analyzed using the correct tools, which can assist you in finding the answers to key SEO queries like:
- What search terms you appear for
- What percentage of users click through to your pages from search results?
- where nation most of your visitors are from
- Which channels generate the most traffic for you?
- How your pages’ visitors interact with them
- What are your most popular pages?
We’ll go through three crucial analytics tools that each website owner should have in order to better understand the fundamentals: Google Search Console, Google Analytics, and a rank tracking tool.
Google Search Console
 Google’s Search Console is a free online tool (or set of tools) that enables webmasters to track their site’s performance in Google Search and improve their websites’ exposure. An indispensable tool that is difficult to replace is Google Search Console. It should be utilized by all website owners.
Google’s Search Console is a free online tool (or set of tools) that enables webmasters to track their site’s performance in Google Search and improve their websites’ exposure. An indispensable tool that is difficult to replace is Google Search Console. It should be utilized by all website owners.
- Performance – provides information on how your website performs in Google Search results.
- URL inspection provides details about any of your pages that Google has indexed.
- Coverage – displays the pages that Google has indexed and alerts users to any indexation problems.
- Sitemaps: These allow you to view your previous submissions and difficulties as well as upload a new sitemap.
- Removals is a tool that lets you momentarily exclude any page from search results.
- Enhancements – gives details on your improvements (such AMP, sitelinks, etc.), as well as difficulties with user experience and usability.
- Shows whether you have received any manual penalties from Google.
- Security concerns – report any security flaws found on your website.
- Links gives a brief summary of your links (both external and internal)
The Performance report is the one we’ll focus on in this chapter and the one you’ll spend the most time with.
Performance report
Your site’s performance in Google Search will be thoroughly outlined in the Performance report.
It has three primary parts that you can customize to display the data you require:
- You can choose the search type, date range, and dimensions using the top filter.
- Clicks, Impressions, Average CTR, and Average Position are the chart’s four major metrics. By clicking on the metrics, you can choose any combination of them.
- Dimension tabs with a data table let you choose your favorite dimension and view the information in a straightforward table.
The Performance report is a treasure of varied additional insights into the search performance of your site outside of the fundamental (but extremely useful) data like top searches or top pages.
Let’s examine a few particular use cases:
Investigate the performance lapses
Always attempt to identify the cause of any change in your performance (such as a sudden decline in clicks) by examining a variety of factors to determine what specifically led to the changes. Sometimes a change in a particular nation, a dip in the rankings for one important keyword, or a performance issue on a particular kind of gadget can have a significant impact on overall results.
Find pages that need the CTR optimization
Take a look at the best-performing inquiries with a low click-through rate (either using the Average CTR metric or comparing the Impressions and Clicks). Writing a better title tag and meta description for the page that ranks for the query has a good likelihood of increasing the CTR.
Compare your performance on desktop and mobile devices
Pick the device dimension in the top filter and then select Compare rather than Filter. You’ll be able to compare how well your site performs on desktop and mobile devices and take the necessary actions to further optimize your site.
Find low-hanging keywords you can rank for easily
Use the filter to limit the dimensions table to just displaying queries that you rank for in position 20 or lower (which means the keyword you rank for on 3rd SERP or higher).
When you locate a keyword of this nature, click the Pages tab to view the page that ranks for it. These are pages that might just require a small amount of optimization to rank higher. A new piece of content that focuses on the keyword might be created or the page that targets it may be improved.
Compare branded and non-branded searches
To display only searches that contain (“queries containing”) your brand name, utilize the top filter. You’ll be able to observe how much of your search traffic is generated by branded keywords and how well they rank in Google.
Google Analytics
 A free website analytics tool called Google Analytics tracks and reports website traffic and user behavior. It is a strong tool that provides a tone of helpful information. The issue is that when opening their GA account, many new users experience confusion and overload. It’s entirely typical. There are too many reports, metrics, and graph types, and the navigating is difficult.
A free website analytics tool called Google Analytics tracks and reports website traffic and user behavior. It is a strong tool that provides a tone of helpful information. The issue is that when opening their GA account, many new users experience confusion and overload. It’s entirely typical. There are too many reports, metrics, and graph types, and the navigating is difficult.
What kind of data can you find in GA?
You may quickly see an overview of the fundamental performance measures on the home dashboard. You can access the detailed reports to obtain additional information. Based on the type of data they contain, the reports are separated into 5 primary types. They are located in the left menu.
- Real-time refers to user action as it occurs in the present moment.
- Everything you need to know about your visitors from the audience (demographics, interests, technology used, etc.)
Acquisition: The source of your traffic (traffic channels, top referring pages, etc.) - Visitor behavior is what people do while on your website (what pages they visit and how they engage with them)
- Information on how your visitors convert, or conversions (in accordance with your goals; e.g. purchase, subscription, affiliate link click, etc.)
Data segmentation
You can further separate the data in each report to receive particular findings that are tailored for your needs. When choosing the appropriate data for your study, segmentation and filtering are essential.
Date range
The first step in using any analytics tool is choosing the appropriate time frame. The date range selector is located in the top right corner of each report. You can use it to view the data over different time periods or contrast two time periods.
Segments
Any subset of data in Google Analytics is a segment. To streamline your workflow, you can choose one of the pre-made segments (such as Organic Traffic or Mobile Traffic) or build and store a new one. To examine the organic reach of your articles independently from other pages, you can establish a special segment that solely displays your organic blog traffic.
Secondary dimension
You can add the secondary dimension to the specified report’s primary dimension as an additional dimension. To examine the percentage of new vs. returning visitors for each page, you may add the User Type secondary dimension to the All Pages report that displays the top pages.
Search
Each data table has a straightforward search field that you may use to get more specific results.
The most useful reports
We would require a separate ultimate guide to cover all the capabilities and data reports that Google Analytics has to offer. However, the vast majority of novice users will succeed if they stick to a few simple reports.
The best ones are listed below:
1. See the most visited pages on your website
One of the main reasons most people use Google Analytics is to check how much traffic their pages receive, and the All Pages report is the most fundamental report available. It helps you identify the topics that visitors to your website are most interested in and decide which pages could use some enhancement.
2. See the first pages people visit on your site
The All Pages report and the Landing Pages report are quite similar, but the Landing Pages report only displays the most popular entry pages for your website. It is also a fantastic report to utilize when examining Google’s organic traffic (the pages people visit from the Search are always landing pages).
3. Find the best sources of your traffic
It is crucial to understand where your traffic is coming from in addition to how well your sites are performing.
There are several sections in the All Traffic report:
- View the percentage of your traffic by the most popular traffic channels using channels (organic, referral, direct, social, etc.)
- See your traffic’s source and the source category (for example, google/organic, bing/organic) by selecting the source/medium option.
- Referrals: View the most popular pages that send visitors to your website
Consider the scenario when you saw an increase in traffic.
To discover which source/medium combination has the greatest growth in users compared to the prior time period, go to the Source/medium report and compare two time periods. Once you’ve located it, you may add a number of secondary dimensions to get further details (for example, the Landing Page secondary dimension to check which pages customers used to access your website or the Country/City secondary dimension based on your target market).
4. Get to know your visitors
Not least, Google Analytics may provide you with information about your audience. Age, gender, and location are the most helpful demographics (countries).
The most useful metrics
There are several metrics available in Google Analytics that gauge three things:
- How many visitors you have (acquisition metrics)
- How users interact with your website (behavior metrics)
- achieving your objectives (conversion metrics)
Traffic acquisition metrics
Here is a quick breakdown of how the most popular traffic acquisition metrics differ from one another: Users: A user is a unique website visitor; subsequent visits from the same user do not increase the overall number of users.
Sessions: A session is a time frame during which a user is actively exploring your website (followed by up to 30 minutes of inactivity); typically, a session lasts for many pages. Every time a visitor accesses a page, a pageview is recorded; if a person accesses the page more than once, several page views are recorded (so the number of pageviews is always higher than the number of sessions).
Bounce rate
The percentage of site visitors that left without taking any further action is represented by the bounce rate measure. Although a high bounce rate isn’t always a bad thing, it’s usually always preferable to have a smaller bounce rate.
Pages per session
This indicator displays the average number of pages a user accessed during a session. The number of pages each session can serve as a reliable gauge of user involvement. Consider techniques to encourage your visitors to visit other pages to increase the ratio:
- Include related products and posts
- Add “more reading” boxes.
- Link to pertinent text pages
Average page time and session length
We don’t advise making any major inferences based on these two time-based Google Analytics measures because they both have accuracy problems. The average time on page is a better measure of how much time visitors spend on your website, if you choose to choose one of them.
Rank tracking
Monitoring your website’s performance in search results for your most essential keywords is known as rank tracking. Rank trackers, in contrast to Google Search Console and Google Analytics, are typically considerably simpler yet very powerful tools.
The main benefits of employing a rank tracker are:
- You may view the positions of your most critical keywords as they change each day.
- Through automatic reporting and alerts, you can rapidly identify any noteworthy ranking spikes or declines.
- In a particular place, you can keep track of your development (e.g. country or city)
- Additionally, you get pertinent metrics to determine the real effects of the adjustments (e.g. the search volumes of the keywords)
- You may keep tabs on your rivals to compare your performance.
Analytics tips and best practices
This chapter will come to a close with some insightful advice on how to efficiently assess your performance.
Track general development while delving into specifics
It’s likely that your performance will change from day to day. Because of this, it’s always wise to consider the wider picture rather than constantly worrying over seemingly insignificant changes. On the other hand, if there is an unexpected change, you virtually never can infer anything from default reporting. To always delve as deeply as you can to discover the root reason is the first guideline of analytics.
Recognize the metrics
To prevent data misunderstanding, keep in mind that you don’t always need to evaluate all the metrics, but it is still beneficial to have a fundamental understanding of what they indicate.
Always make an effort to grasp the context
Don’t take the evidence at face value; instead, consider the causes of what occurred. For instance, there may be a number of internal and external factors to consider while troubleshooting ranking drops:
- new updates to the website
- Updated Google algorithm
- technical difficulties or website downtime
- Google’s manual process
- The rank tracking tool has a bug.
You should have a better understanding of the issue after carefully reviewing Google Search Console, Google Analytics, and your rank tracker. As a result, you’ll be more equipped to choose your next course of action.
Is Offpage SEO still there?
Although “off-page SEO” and “link building” were frequently used interchangeably in the past, there are also numerous other off-page SEO strategies you may employ, such as brand building, citation building, and content marketing.
What is Offpage SEO?
Off-page SEO is a sort of search engine optimization that raises a website’s or page’s rankings in pertinent search results using off-site adjustments. Off-site optimizations take place away from your website and include things like link development and local citations. Off-Page SEO Services can be seen.
What is difference between on-page SEO and off-page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to SEO elements and methods that are concentrated on improving elements of your website that you have control over. Off-page SEO refers to SEO elements and tactics used to spread the word about your website or business online.
How many backlinks do I need to rank?
The difficulty ranking increases more slowly than the quantity of backlinks required. For instance, you most likely need roughly 10 backlinks to rank for a term with a difficulty score of 10. To rank, though, you might need 100 backlinks if the difficulty is 50.
